Linked List in JavaScript
What is a Data Structure?
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that is usually chosen for efficient access to data.
What is Linked List?
🧠 A linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory.
A node(element in Linked List) has its data and reference to the next item
Let’s Break it Down🤩
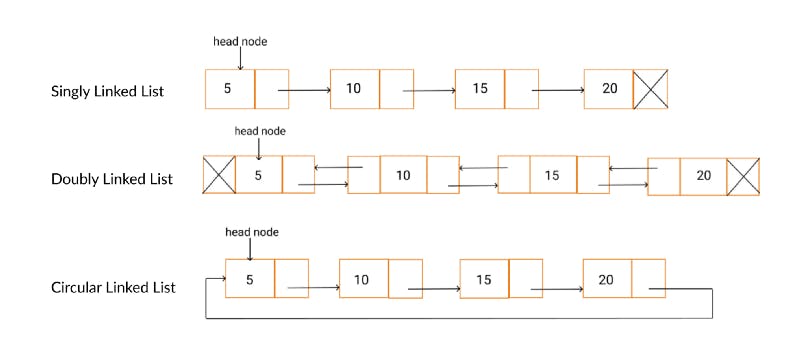
What are the types of Linked List?
- Singly LinkedList
- Doubly Linked List
- Circular Linked List
Picture speaks louder than words:👇🏻
What is Node in a Linked List?
A linked List is a collection of connected nodes where the node is something that has the data part as well as the link to the next node.
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data=data;
this.next=null}
}
How to implement Linked List?
In a Linked list, mostly what we know is the head node; from the head node, we can get the other remaining nodes. Head node is the first node in a linked list. We can also maintain a tail node in order to make operations faster.
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head=null;
this.tail=null;
}
}
We have our Node as well as LinkedList Class.
Now let’s begin the actual fun by adding data to our linked list.
Let’s add a new Node to our Empty LinkedList.
Add a single node
✓ This is how you add a single node to LinkedList

✓ Let’s make a function to add a node at the head
Add a new node at the head
While adding a new node, the new Node should point to the current head Node and then the head should point to the new node
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head=null;
this.tail=null;
}
addElementatHead(key) {
let node = new Node(key);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
return;
} else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
}
}
Add a new node at the End Of a Linked List
//inside class
addElemenAtEnd(key) {
let node = new Node(key);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
return;
} else {
let temp = this.head;
while (temp.right !== undefined) {
temp = temp.right;
}
temp.right = node;
}
Traverse through Linked List
//inside class linkedlist as a method
traverse() {
let temp = this.head;
// console.log(temp.next);
while (temp?.key != undefined) {
console.log(temp.key);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
Remove at Head
removeathead(){
let temp = this.head;
this.head = temp.next;
temp = null;
}
Hope this detailed thread was useful. Follow me on Medium as well as on my Twitter handle Adarsh Gupta for more content around JavaScript, Web Development, DSA, and more.
I will be posting on data structures and algorithms so don't miss this opportunity. Start learning DSA and tag me on Twitter if you learned something from me.

